Blog
Insights
12 Mobile app development free software You Should Know
Discover the top 12 mobile app development free software strategies and tips. Complete guide with actionable insights.

Nafis Amiri
Co-Founder of CatDoes

Building a mobile app no longer requires a massive budget or an extensive in-house development team. The market is filled with powerful, free software that empowers everyone from startup founders and business owners to students and hobbyists to bring their ideas to life. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the best mobile app development free software available today, helping you select the right tool for your specific project, technical skill level, and long-term goals.
We will explore a curated list of integrated development environments (IDEs), cross-platform frameworks, and innovative AI-native platforms. Each entry includes a concise description, a breakdown of core features, honest pros and cons, and practical best-use scenarios. To help you get started quickly, we've also included direct download links and essential setup tips for every tool.
This resource is designed to cut through the noise and provide clear, actionable information. Whether you are building a native iOS or Android app, or targeting both platforms simultaneously, you will find a solution that fits. For those aiming to reach a wider audience across different operating systems, consider exploring various cross-platform mobile development tools to maximize your reach efficiently. Our goal is to equip you with the knowledge to make an informed decision and begin your app development journey with confidence.
1. CatDoes
CatDoes positions itself as a uniquely powerful AI-native platform, designed to transform plain-language ideas into fully functional, production-ready mobile applications. This platform represents a significant leap in mobile app development free software, moving beyond simple UI builders to offer a true end-to-end automated solution. Its multi-agent system intelligently handles the entire development lifecycle, from initial concept to deployment, making it an exceptional choice for founders, agencies, and engineers aiming for unprecedented speed and efficiency.
What sets CatDoes apart is its holistic, agent-driven workflow. A Requirements agent first captures your specifications through natural language. Next, a Designer agent generates polished, professional UI themes, and then Software agents write the business logic in React Native Expo. This process culminates in a cross-platform app you can immediately preview in-browser or test on a physical device using a QR code.
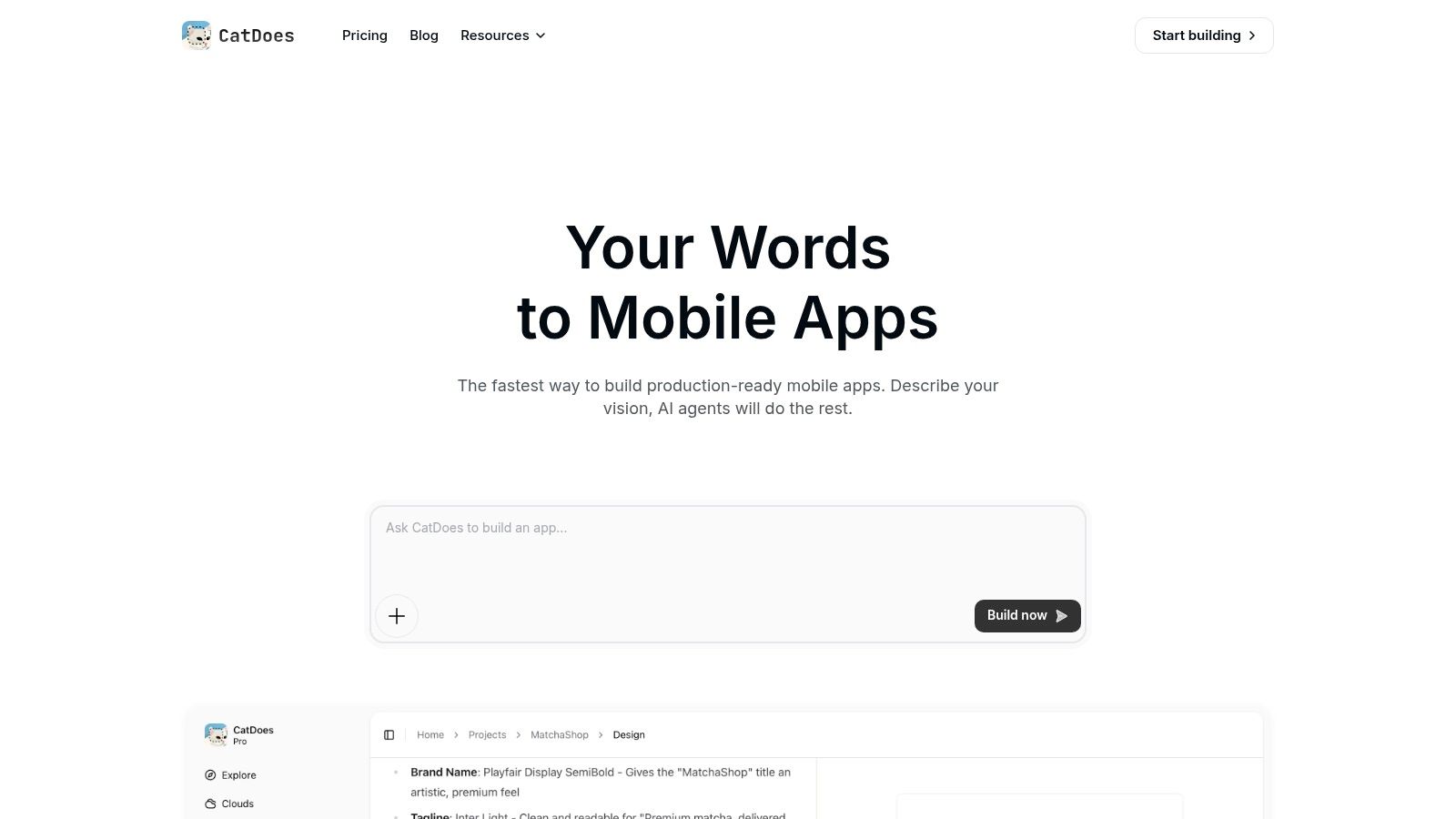
Core Strengths and Use Cases
The platform's standout feature is the AI-configured managed backend, CatDoes Cloud. The AI agents don't just build the frontend; they provision and configure all necessary backend services, including authentication, databases, file storage, and edge functions. This integrated approach eliminates the complex and time-consuming task of manual backend setup, ensuring the frontend and backend are perfectly synchronized from the start.
Additional enterprise-grade features like built-in error monitoring (CatDoes Watch) and an automated build-and-release agent solidify its professional credentials. Optional GitHub integration allows development teams to maintain a remote repository, blending AI speed with traditional version control workflows.
Best For:
Startup Founders & Entrepreneurs: Rapidly build and launch MVPs to test market fit.
Non-Technical Creators: Turn ideas into functional apps without writing a single line of code.
Developers & Agencies: Accelerate project timelines and automate repetitive setup tasks.
Businesses: Create internal tools or B2C applications with minimal development overhead.
Limitations and Pricing
While incredibly powerful for most applications, CatDoes may not be the ideal solution for apps requiring highly specialized, low-level native code or obscure platform-specific SDKs. Complex, granular customizations might still necessitate manual intervention by an engineer.
CatDoes offers a generous free tier that allows you to build one complete application, making it accessible for single projects or evaluation. For building multiple apps or accessing advanced features, tiered subscription plans are available. Teams should consult the official website for detailed pricing and usage limits.
Website: https://catdoes.com
2. Android Studio (Google)
For anyone serious about building native Android applications, Android Studio is the definitive and official Integrated Development Environment (IDE) from Google. It's the industry-standard mobile app development free software for the Android platform, providing a complete suite of tools to write, debug, test, and package apps specifically for Google’s ecosystem. It is completely free to download and use, requiring only a compatible Windows, macOS, or Linux machine.
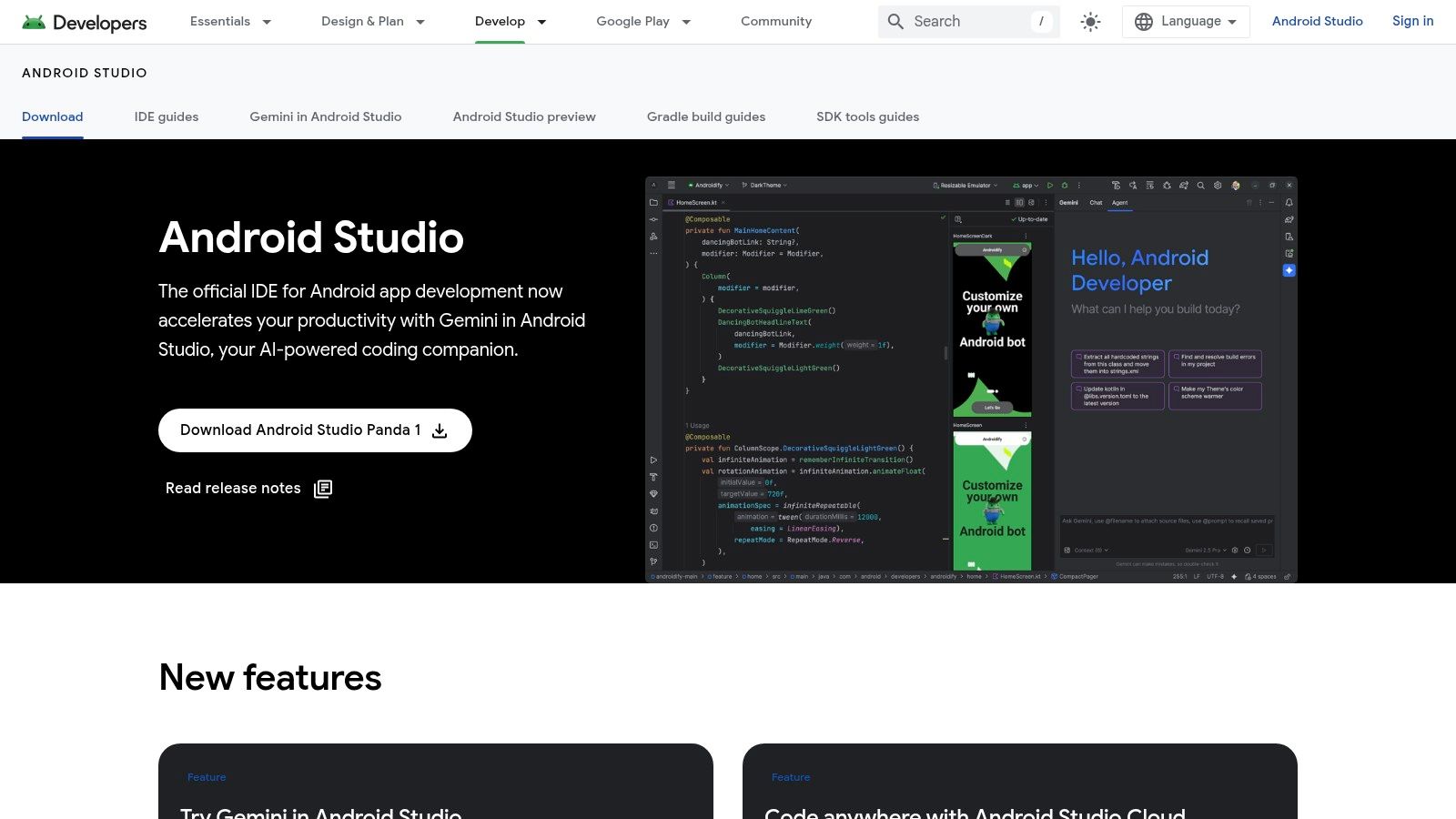
This platform stands out because it offers first-party support, meaning developers get the fastest access to new Android APIs, features, and OS updates. The user experience is tailored for deep, performance-oriented development. It includes powerful tools like the Layout Inspector for real-time UI debugging, a robust profiler to diagnose performance bottlenecks, and a versatile emulator to test on thousands of virtual device configurations. The recent integration of the Gemini AI assistant directly within the IDE provides intelligent code completion, bug fixing, and generation, significantly accelerating the development workflow.
Core Features
Intelligent Code Editor: Provides advanced code completion, refactoring, and static analysis for Java, Kotlin, and C++.
Flexible Build System: Utilizes a Gradle-based system for managing dependencies and creating multiple build variants.
Comprehensive Testing Suite: Includes a built-in Android Emulator, performance profilers, and APK/App Bundle analyzers.
Visual Layout Editor: Features a drag-and-drop UI designer with live previews for Jetpack Compose.
Integrated AI Assistant: Gemini in Android Studio helps generate code, explain snippets, and fix errors.
Pros and Cons
Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
Direct, first-party support from Google | High system resource consumption |
Fastest access to new Android SDK features | Steep learning curve for beginners |
Best-in-class debugging and performance profiling tools | Exclusive to Android; no native iOS build support |
Free and open source with a massive community | Gradle build times can be slow for large, complex projects |
Who is Android Studio Best For?
Android Studio is the go-to choice for developers focused exclusively on creating high-performance, feature-rich native Android applications. It's ideal for teams that need to leverage the very latest Android platform capabilities and require deep, granular control over app performance and hardware integration. If your project demands the absolute best native experience on Android, this is the tool to use.
3. Xcode (Apple)
For developers building apps within Apple's ecosystem, Xcode is the essential and official Integrated Development Environment (IDE). It is the cornerstone of mobile app development free software for iOS, iPadOS, macOS, watchOS, tvOS, and visionOS. Xcode provides a complete toolkit for designing, developing, testing, and debugging applications specifically for Apple devices. The software itself is a free download from the Mac App Store, though it requires a macOS-based computer to run.
This platform's primary advantage is its first-party status, guaranteeing immediate access to the latest Apple SDKs, Swift language updates, and SwiftUI features. The user experience is tightly integrated with the entire Apple development workflow, from coding to deployment. It includes powerful Simulators for testing on various Apple devices, a sophisticated performance analysis tool called Instruments, and seamless integration with TestFlight for beta testing. This tight integration is crucial for creating a true native mobile application that meets Apple's high standards for performance and user experience.
Core Features
Advanced Code Editor: Offers intelligent code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging for Swift and Objective-C.
Interface Builder: A visual tool for designing and building user interfaces with storyboards or SwiftUI previews.
Comprehensive Simulators: Includes a vast library of simulators for every iPhone, iPad, Apple Watch, and Apple TV model.
Instruments Profiling Tool: Provides in-depth analysis of performance, memory usage, and energy consumption.
Integrated Source Control: Built-in support for Git to manage version control directly within the IDE.
Pros and Cons
Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
Direct, first-party support from Apple | Exclusively available on macOS |
Fastest access to new iOS, iPadOS, and visionOS features | Paid Apple Developer Program membership needed for App Store |
Deep debugging and performance profiling with Instruments | Can be complex and intimidating for absolute beginners |
Free to download and use for development and testing | Build processes can be resource-intensive on older Mac hardware |
Who is Xcode Best For?
Xcode is the non-negotiable choice for developers, teams, and businesses focused on creating high-quality, high-performance native applications for Apple's platforms. It is indispensable for anyone wanting to leverage the latest hardware and software capabilities of iPhones, iPads, and other Apple devices. If your goal is to deliver a premium, fully optimized experience to users in the Apple ecosystem, Xcode is the definitive tool.
4. Flutter (Google)
For developers aiming to build beautiful, natively compiled applications for mobile, web, and desktop from a single codebase, Flutter is Google's open-source UI software development kit. It has rapidly become a leading mobile app development free software by empowering teams to create high-fidelity, high-performance apps for iOS and Android using one language, Dart. Flutter is entirely free to download and use on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
The platform's standout feature is its "write once, run anywhere" philosophy, which does not sacrifice performance or visual fidelity. Flutter achieves this by using its own high-performance rendering engine to draw widgets directly to the screen, ensuring a consistent look and feel across platforms. The developer experience is defined by its "Hot Reload" capability, allowing developers to see the effect of code changes in real-time without restarting the app. This feature dramatically speeds up UI building, bug fixing, and experimentation, making development faster and more interactive.
Core Features
Single Codebase: Build, test, and deploy apps for iOS, Android, web, and desktop from one Dart codebase.
Stateful Hot Reload: Instantly view code changes in your running app, preserving its current state for rapid iteration.
Expressive UI Toolkit: Offers a rich catalog of customizable widgets that deliver native-like performance.
Native Performance: Compiles to ARM or Intel machine code as well as JavaScript for fast performance on any device.
Extensive Documentation: Features comprehensive official guides, codelabs, and a vibrant community.
Pros and Cons
Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
High developer velocity and rapid UI iteration | Requires learning the Dart programming language |
Excellent performance with a consistent look across platforms | Apps can have a larger file size compared to native builds |
Strong backing from Google and a large, active community | Platform-specific integrations can sometimes be complex |
Completely free and open source with a rich package ecosystem | The talent pool for Dart is smaller than for Swift or Kotlin |
Who is Flutter Best For?
Flutter is ideal for startups, SMBs, and development teams that need to launch a visually appealing app on both iOS and Android simultaneously with limited resources. It's a perfect choice for projects where brand-centric UI and a consistent user experience across platforms are top priorities. Developers who value extremely fast development cycles and the ability to iterate quickly on user feedback will find Flutter’s Hot Reload feature invaluable.
5. React Native (Meta + community)
React Native is a popular open-source framework from Meta that empowers web developers to build truly native iOS and Android apps using their existing JavaScript and React skills. This powerful mobile app development free software allows teams to write most of their application logic once and deploy it on both major platforms. It is completely free, relying on the MIT license, and only requires a standard development environment with Node.js.

This framework stands out by bridging the gap between web technologies and native performance. Instead of rendering web components in a WebView, React Native uses fundamental UI building blocks that are compiled directly to native platform widgets. This "learn once, write anywhere" approach accelerates development without sacrificing the look, feel, and performance of a native application. For a detailed comparison with other cross-platform tools, exploring a Flutter vs. React Native breakdown for 2026 can provide deeper insights into which framework might be a better fit for your project.
Core Features
Native UI Components: Renders to native platform UI, not webviews, for a genuine native user experience.
JavaScript & React-Based: Leverages one of the most popular web development ecosystems, including extensive npm libraries.
TypeScript Support: Offers full compatibility with TypeScript for building robust, scalable, and type-safe applications.
Fast Refresh: See your edits in seconds without losing your application's state, dramatically speeding up the UI development process.
Large Community: Backed by a massive global community and Meta, ensuring a rich collection of libraries, tools, and tutorials.
Pros and Cons
Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
Familiar to web and React teams, reducing the learning curve | Occasionally requires native code for complex integrations |
Codebase can be shared across iOS, Android, and web | Upgrading between versions can be complex for large projects |
Huge ecosystem of third-party libraries and tools | Performance may lag behind true native in intensive tasks |
Free, open-source, and backed by Meta | The quality of third-party libraries can be inconsistent |
Who is React Native Best For?
React Native is the ideal choice for web development teams, especially those already proficient in React, who want to build mobile apps efficiently. It's perfect for startups and businesses aiming to create a cross-platform MVP quickly without hiring separate iOS and Android developers. If your project prioritizes code sharing and faster development cycles over accessing the most niche, platform-specific APIs, React Native is an excellent and cost-effective solution.
6. Expo (for React Native)
For developers using React Native, Expo provides an open-source framework and platform that dramatically simplifies the development process. It's a layer built around React Native that smooths over the complexities of native configuration, allowing you to write universal JavaScript/TypeScript code that runs on Android, iOS, and the web. Expo offers a suite of mobile app development free software tools, including its powerful SDK and the Expo Go app, which makes it one of the fastest ways to go from a new project to a running app on a physical device.
Expo stands out by creating the easiest possible on-ramp to mobile development. Its managed workflow handles much of the native project setup, letting you focus entirely on the React Native code. The user experience is phenomenal for rapid prototyping; developers can scan a QR code with the Expo Go companion app and see their project running and updating live on their phone in seconds. This eliminates the need for Xcode or Android Studio during the initial development phases, which significantly lowers the barrier to entry for web developers and beginners.
Core Features
Expo Go Companion App: Instantly preview and test your apps on physical Android and iOS devices without native build tools.
Managed Workflow: Abstracts away complex native project configurations for a pure JavaScript/TypeScript experience.
Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates: Push updates directly to users' devices without needing a full app store resubmission.
Expo Application Services (EAS): Optional cloud services for building, submitting, and updating your apps.
Extensive SDK: Provides access to device APIs like camera, notifications, and file system through a unified library.
Pros and Cons
Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
Fastest way to start and prototype with React Native | Some native libraries are not compatible with the Expo Go app |
Eliminates the need for Xcode/Android Studio for basic development | Heavy use of EAS cloud services may require a paid subscription |
Simplified OTA updates and build processes | Less granular control over native modules than a bare React Native app |
Excellent documentation and strong community support | Ejecting to a bare workflow can add complexity |
Who is Expo Best For?
Expo is the ideal choice for developers, startups, and students who want to build cross-platform mobile apps with React Native as quickly as possible. It is perfect for those building MVPs, prototyping ideas, or for teams with a strong web development background transitioning to mobile. If your project prioritizes speed of iteration and a simplified developer experience over deep native customization, Expo is the best place to start.
7. Visual Studio Community + .NET MAUI (Microsoft)
For developers already invested in the Microsoft ecosystem, Visual Studio Community combined with .NET MAUI presents a powerful and familiar environment. This pairing offers a complete mobile app development free software solution for building native, cross-platform applications from a single C# codebase. Visual Studio Community is a full-featured IDE that is free for individual developers, open-source projects, and small teams, providing access to professional-grade tools for creating apps for iOS, Android, Windows, and macOS.
What makes this combination stand out is its deep integration and the productivity it offers to C# and .NET developers. Instead of learning multiple languages and frameworks, a team can leverage its existing C# skills to target every major mobile and desktop platform. .NET MAUI (Multi-platform App UI) allows developers to write UI code once that renders as native controls on each target platform, ensuring high performance and a platform-appropriate look and feel. The Visual Studio IDE provides a world-class debugging experience, rich code editing with IntelliSense, and powerful profiling tools to optimize app performance.
Core Features
Cross-Platform UI with .NET MAUI: Write a single UI layer in XAML or C# that maps to native controls on Android, iOS, macOS, and Windows.
Rich Visual Studio IDE: Utilizes a best-in-class debugger, profilers, designers, and code analysis tools.
Large .NET Ecosystem: Access a massive collection of libraries, packages, and components via NuGet to extend app functionality.
Single Project Structure: Manage all platform-specific assets and code within one unified project for streamlined development.
Hot Reload: Instantly see changes made to your XAML or C# code in the running application without needing to recompile.
Pros and Cons
Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
Strong C# tooling and productive experience for .NET teams | macOS machine is required for final iOS app signing and building |
Write once, run everywhere on mobile and desktop | MAUI project setup can feel heavier than web-stack frameworks |
Mature documentation, samples, and training resources | The IDE can have high system resource requirements |
Free Community license is generous for small teams | The learning curve can be steep for those new to the .NET ecosystem |
Who is Visual Studio Community + .NET MAUI Best For?
This combination is the perfect choice for individual developers or small teams that have a background in C# and .NET. It is ideal for businesses looking to build cross-platform applications that share a significant amount of code between mobile and desktop versions. If your team wants to leverage its existing Microsoft-stack expertise to build true native apps efficiently, this is the most direct and powerful path.
8. Kotlin Multiplatform (JetBrains)
For development teams already proficient in Kotlin, Kotlin Multiplatform (KMP) presents a powerful and efficient approach to cross-platform development. This open-source technology from JetBrains allows developers to share common business logic, data layers, and connectivity code across both Android and iOS while retaining fully native user interfaces. As a leading mobile app development free software framework, KMP offers a pragmatic balance: write shared code once in Kotlin and then build platform-specific UIs using Jetpack Compose for Android and SwiftUI for iOS.

What makes KMP stand out is its principle of "expect-actual" mechanisms, enabling shared code to access native APIs and libraries directly. This means you don't sacrifice performance or access to platform-specific features like sensors or device storage. The framework is designed for incremental adoption, so teams can start by sharing a small module, like a network layer, and expand its usage over time without a complete rewrite. This flexibility makes it a strategic choice for modernizing existing native apps or starting new projects with a focus on code reuse and native performance.
Core Features
Shared Business Logic: Write common code once in Kotlin for Android, iOS, and other platforms.
Native API Access: Interoperate seamlessly with platform-specific APIs and SDKs from shared Kotlin code.
Flexible UI Options: Keep native UIs (SwiftUI/XML) or use Compose Multiplatform for a shared UI layer.
Incremental Adoption: Can be integrated into existing native projects one module or feature at a time.
Excellent Tooling: Leverages Android Studio and IntelliJ IDEA with dedicated KMP plugins for a unified workflow.
Pros and Cons
Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
Achieves native performance on both Android and iOS | Still requires Xcode and macOS for building the iOS app |
Allows for maximum code reuse without sacrificing native feel | Has a learning curve for teams unfamiliar with Kotlin/Gradle |
Strong developer experience within the JetBrains ecosystem | The ecosystem is still maturing compared to other frameworks |
Free, open-source, and backed by Google and JetBrains | Finding developers with KMP expertise can be challenging |
Who is Kotlin Multiplatform Best For?
Kotlin Multiplatform is ideal for development teams with existing Kotlin expertise, especially those primarily focused on Android who want to extend their reach to iOS efficiently. It is perfect for projects that require high performance and deep integration with native platform features but also want to avoid duplicating complex business logic. If your team values code reuse but refuses to compromise on a truly native user experience, KMP provides an excellent and modern solution.
9. NativeScript
NativeScript is an open-source framework that empowers web developers to build truly native mobile apps using languages they already know, such as JavaScript, TypeScript, Angular, or Vue.js. Unlike solutions that rely on a WebView, this mobile app development free software compiles your code to native UI components, providing direct access to iOS and Android APIs. This means you can achieve native performance and user experience without writing a single line of Swift, Objective-C, Java, or Kotlin.
This platform stands out by bridging the gap between web technologies and native mobile performance. It provides one hundred percent day-one access to new platform APIs, ensuring your app can leverage the latest hardware and software features immediately. For teams with strong web development skills, NativeScript offers a significantly lower barrier to entry into the native mobile world compared to learning entirely new programming languages and ecosystems. The command-line interface (CLI) and extensive community plugin market streamline the development and integration process.
Core Features
Direct Native API Access: Call iOS and Android APIs directly from your JavaScript or TypeScript code.
Web Framework Integration: Build apps using popular frameworks like Angular and Vue.js for a familiar workflow.
Cross-Platform UI: Write a single UI codebase that renders as native platform-specific controls.
Powerful CLI: A robust Command Line Interface for creating, building, and deploying applications.
Extensible with Plugins: A rich ecosystem of community-driven plugins to add native functionality.
Pros and Cons
Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
Achieve native performance using web technologies | Smaller community and ecosystem than React Native or Flutter |
Zero-day access to new native platform APIs | Can have a learning curve for complex native integrations |
Re-use of skills for web developers (JS, TS, Angular, Vue) | Upgrading between major versions can be challenging |
Completely free and open source | Some advanced UI patterns may require native-level knowledge |
Who is NativeScript Best For?
NativeScript is an excellent choice for web development teams and individuals who want to create high-performance, native mobile applications without leaving their JavaScript or TypeScript ecosystem. It is ideal for projects that require deep integration with native device features, such as accessing specific sensors or platform APIs that are not easily available through other cross-platform tools. If your team is proficient in Angular or Vue.js, NativeScript provides the most direct path to building a truly native app.
10. Ionic Framework + Capacitor (Ionic)
For web developers aiming to enter the mobile space, Ionic provides one of the most direct paths. It's a free, open-source UI toolkit that allows you to build cross-platform native apps using standard web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript with frameworks such as Angular, React, or Vue. Paired with Capacitor, its official successor to Cordova, Ionic wraps your web app in a native shell, granting it access to device hardware APIs for iOS, Android, and Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) from a single codebase.
This platform excels by lowering the barrier to entry, allowing web development teams to leverage their existing skills and tools without learning Swift or Kotlin. The core value is its "write once, run anywhere" philosophy, powered by a rich library of pre-built UI components that adapt to platform-specific design languages. Capacitor acts as the bridge to native functionality, providing a modern, npm-based workflow to access device features like the camera, geolocation, and push notifications through a simple plugin system. This combination makes Ionic a powerful piece of mobile app development free software.
Core Features
Web-First UI Toolkit: A comprehensive library of UI components, gestures, and theming options that adapt to iOS and Android.
Capacitor Native Runtime: Provides a robust API to access native device features and package web apps for app stores.
Framework Agnostic: Officially supports Angular, React, and Vue, along with options for vanilla JavaScript.
Unified Codebase: Share code across iOS, Android, and Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) to maximize efficiency.
Command Line Interface (CLI): A powerful CLI simplifies project creation, development, and building processes.
Pros and Cons
Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
Lowest friction for existing web development teams | Performance can lag behind true native for intensive apps |
Easy, npm-based workflow and development process | Some native UX nuances can be hard to replicate in a WebView |
Mature documentation and large community plugin ecosystem | Enterprise-level services and support options can vary |
Free and open source core framework | Can have limitations for apps requiring deep OS integration |
Who is Ionic Framework + Capacitor Best For?
Ionic is the ideal choice for web developers and teams who want to build mobile apps without abandoning their existing technology stack. It's perfect for creating content-driven applications, utility apps, and business-focused tools where rapid development and code reuse across platforms are top priorities. If your project benefits from a shared codebase between your website, PWA, and mobile apps, Ionic offers an incredibly efficient solution.
11. Apache Cordova
Apache Cordova is one of the original open-source frameworks that pioneered the hybrid app development model. It enables developers to build cross-platform mobile apps using standard web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, then wrapping them in a native container. This mobile app development free software acts as a bridge, allowing web code to run within a native WebView and access device-specific functions like the camera or accelerometer through a vast ecosystem of plugins. It is completely free and maintained by the Apache Software Foundation.

Cordova stands out for its longevity and its "write once, run anywhere" philosophy, making it an excellent choice for web developers looking to enter the mobile space without learning native languages. The platform’s core strength lies in its extensive plugin architecture. Developers can leverage a command-line interface (CLI) to easily add plugins that expose native APIs, effectively extending the capabilities of a standard web application to match those of a native app. This approach is particularly useful for content-driven apps or for porting existing web projects to mobile platforms with minimal effort.
Core Features
Web-Based Development: Uses HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScript to build the core application logic and UI.
Cross-Platform Codebase: A single codebase can be deployed to both iOS and Android, saving time and resources.
Extensive Plugin Ecosystem: Provides access to native device features through a large library of open-source plugins.
Command-Line Interface (CLI): A powerful CLI streamlines project creation, platform management, and plugin installation.
Hosted by Apache: Backed by the Apache Software Foundation, ensuring it remains a free and open-source project.
Pros and Cons
Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
Easy for web developers to adopt and get started | Performance can be lower than truly native frameworks |
Proven, mature technology with a large knowledge base | User experience can feel less "native" due to WebView |
One codebase targets multiple platforms | Plugin quality and maintenance can be inconsistent |
Free and open source | Less popular now compared to modern alternatives like React Native |
Who is Apache Cordova Best For?
Apache Cordova is ideal for developers and teams with strong web development skills who need to create simple, content-focused apps for multiple platforms quickly. It is a practical choice for building proof-of-concept projects, internal business applications, or apps where leveraging an existing web codebase is a primary goal. If your app does not require high-performance graphics or complex native UI integrations, Cordova offers a fast and cost-effective path to the app stores.
12. MIT App Inventor
MIT App Inventor is a revolutionary, web-based tool designed to democratize app creation, making it accessible to everyone, regardless of their coding background. It uses a visual, block-based programming language, allowing users to build fully functional Android and iOS apps by dragging and dropping components. This intuitive approach makes it a standout piece of mobile app development free software, particularly for educational purposes, rapid prototyping, and for beginners taking their first steps into app development. It is completely free to use.
The platform stands out because of its incredibly low barrier to entry. Unlike traditional IDEs that require complex setup and coding knowledge, App Inventor lets you build an app in a browser and test it live on your device in minutes using the MIT AI2 Companion app. The user experience is focused on simplicity and immediate feedback, empowering non-programmers to bring their ideas to life. The extensive library of tutorials and a strong educational community provide a supportive environment for learning and experimentation.
Core Features
Visual Blocks Programming: Build app logic by connecting puzzle-like blocks instead of writing traditional code.
Drag-and-Drop UI Designer: Visually lay out your app's user interface with buttons, images, and other components.
Live Testing: Instantly see changes on your Android or iOS device through the companion app.
Extensive Component Library: Includes access to device features like GPS, accelerometer, and camera.
Comprehensive Educational Resources: Offers free, detailed tutorials, curricula, and guides for all skill levels.
Pros and Cons
Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
Extremely easy to learn; perfect for beginners and students | Not suitable for complex, high-performance, or large-scale apps |
Fast prototyping and instant testing on real devices | Limited access to advanced native APIs and platform integrations |
Completely free with no hidden costs | UI customization can be less flexible than with native development |
Strong focus on education with a massive resource library | Performance may not be on par with natively coded applications |
Who is MIT App Inventor Best For?
MIT App Inventor is the ideal starting point for students, educators, hobbyists, and anyone with a great app idea but no formal programming experience. It is also an excellent tool for developers and designers who need to quickly create a functional prototype to validate a concept or demonstrate core functionality. If the goal is learning, teaching, or rapid idea-to-app execution without writing code, this platform is an unparalleled choice.
12 Free Mobile App Development Tools: Feature Comparison
Platform | Core features | Quality / Ease (★) | Value & Pricing (💰) | Target audience (👥) | Unique strengths (✨) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CatDoes 🏆 | AI multi‑agent: requirements → design → React Native Expo code + managed backend, live preview, automated builds | ★★★★★ (conversational, fast) | 💰 Free (1 app) + tiered subs; reduces dev time-to-market | 👥 Non‑technical creators, startups, engineers, agencies | ✨ End‑to‑end AI automation (design, backend, build & release) |
Android Studio (Google) | Official Android IDE: emulator, SDK/NDK, profilers, Jetpack Compose tooling | ★★★★☆ (robust for Android) | 💰 Free; best for Android‑first projects | 👥 Android developers, platform teams | ✨ First‑party access to latest Android features & tooling |
Xcode (Apple) | Apple IDE: Swift/SwiftUI, simulators, Instruments, signing & TestFlight integration | ★★★★☆ (essential for iOS) | 💰 Free; App Store publishing needs paid Apple Developer | 👥 iOS/macOS developers, native Apple apps | ✨ Deep Apple platform integration and profiling tools |
Flutter (Google) | Single Dart codebase for mobile/web/desktop, rich widgets, Hot Reload | ★★★★☆ (fast UI iteration) | 💰 Free; strong ecosystem | 👥 Teams wanting consistent cross‑platform UI | ✨ High‑fidelity UI + rapid Hot Reload iteration |
React Native (Meta + community) | React + JS/TS → native UI components, large npm ecosystem | ★★★★☆ (web dev friendly) | 💰 Free; flexible tooling choices | 👥 Web/React developers, startups | ✨ Familiar React patterns and broad library support |
Expo (for React Native) | Expo Go for instant testing, EAS builds/submit/update, managed workflow | ★★★★☆ (fast prototyping via QR) | 💰 Free core; paid EAS for heavy CI/CD | 👥 Beginners, prototypers, React Native teams | ✨ QR preview & easiest path to on‑device testing |
Visual Studio + .NET MAUI (Microsoft) | C# cross‑platform UI, VS debugger/profilers, .NET ecosystem | ★★★☆☆ (strong for .NET teams) | 💰 Free Community (license limits); enterprise options | 👥 .NET/C# teams, enterprise apps | ✨ Mature C# tooling and Windows support |
Kotlin Multiplatform (JetBrains) | Share business logic across iOS/Android, native APIs, Compose Multiplatform | ★★★☆☆ (native performance) | 💰 Free; macOS required for iOS builds | 👥 Kotlin/Android teams seeking native UX | ✨ Incremental adoption with native performance |
NativeScript | Direct native API bindings from JS/TS (Angular/Vue support), CLI via npm | ★★★☆☆ (native access from web stack) | 💰 Free; smaller ecosystem | 👥 Web devs needing direct native APIs | ✨ Call native platform APIs without WebView |
Ionic + Capacitor (Ionic) | Web‑first UI toolkit + Capacitor for native plugins & PWAs | ★★★☆☆ (fast web‑to‑mobile) | 💰 Free core; enterprise services vary | 👥 Web teams, PWAs, cross‑platform prototypes | ✨ Low friction for web teams; strong plugin ecosystem |
Apache Cordova | HTML/CSS/JS wrapped with plugins for native features (legacy hybrid) | ★★☆☆☆ (dated WebView UX) | 💰 Free; proven legacy approach | 👥 Web developers, legacy projects | ✨ Mature, historically broad plugin base |
MIT App Inventor | Visual blocks programming, drag‑and‑drop UI, live companion testing | ★★☆☆☆ (education & prototyping) | 💰 Free; education focus | 👥 Beginners, students, educators | ✨ Extremely low barrier; ideal for learning/prototypes |
Final Thoughts
Navigating the world of mobile app development free software can feel overwhelming, but as we have explored, the ecosystem is rich with powerful, accessible, and cost-effective solutions. The journey from a simple idea to a fully functional application on a user's device has never been more achievable, thanks to the robust tools available at no initial cost. We have covered a wide spectrum, from the native powerhouses of Android Studio and Xcode to the cross-platform efficiency of Flutter and React Native, and the revolutionary speed of AI-native platforms like CatDoes.
The key takeaway is that there is no single "best" free tool; instead, there is only the best tool for your specific project. Your choice hinges on a careful evaluation of your goals, technical skills, target audience, and long-term vision. A solid understanding of these factors will guide you to the right starting point.
Choosing Your Path: A Final Decision Framework
To crystallize your decision, consider these final guiding questions before you commit to a platform:
Who is building the app? If you are a non-technical founder or a designer, a low-code or AI-native platform like CatDoes or a visual builder like MIT App Inventor offers the most direct path to a functional product. If you have a team of developers with web experience, frameworks like React Native or Ionic are a natural fit.
What is the core purpose of the app? For applications that require deep integration with device hardware or demand the highest possible performance, native development with Android Studio and Xcode remains the gold standard. For content-driven apps or MVPs where speed to market is critical, cross-platform solutions provide unmatched efficiency.
What is your long-term plan? Think beyond the initial build. Consider the community support, the ease of finding developers, and the scalability of the platform. Frameworks backed by major corporations like Google (Flutter) and Meta (React Native) often have extensive documentation, a large talent pool, and a clear roadmap for future development.
From Development to Deployment
Remember that building the application is only part of the process. Once your mobile app is developed, understanding the deployment process is essential, and you can find guides on how to deploy apps from Google AI Studio for specific scenarios. Each platform has its own set of procedures for packaging, signing, and submitting your app to the Apple App Store and Google Play Store. Be sure to research these requirements early on to avoid last-minute hurdles.
The vibrant landscape of mobile app development free software in February 2026 empowers creators, entrepreneurs, and developers to bring their visions to life without significant upfront investment. By aligning your project needs with the strengths of the tools discussed, you can confidently embark on your development journey, build a high-quality application, and make your mark in the competitive mobile marketplace. The power to create is truly at your fingertips.
Ready to turn your idea into a market-ready app in a fraction of the time? Explore CatDoes, the AI-native platform that generates production-quality code from your designs, bypassing the complexities of traditional development. Start building your dream app today with the power of AI. Visit CatDoes to learn more.

Nafis Amiri
Co-Founder of CatDoes


